Ethereum will die without Ethereum 2.0!

You may be familiar with the children’s game “red light, green light”. This entertainment is a popular game among children. When they hear the phrase “green light”, they run towards the finish line, and when they hear the phrase “red light”, they must stop in the same condition and state they are in; Otherwise, they will be removed from the game cycle.
Now the competition between digital currencies is like this game. The green lights are the popular bullish markets and the red lights are the bloody red and bearish days of this market. Cryptocurrencies that cannot survive the red light or those that cannot cross the finish line will be removed from the market cycle. Whether we like it or not, these are the conditions and rules of the game.
Meanwhile, some players may cheat and hide behind other players. Some may be afraid to move, and some weaker players may imitate their decisions from stronger players. In this chaos, we see a dramatic situation. A player who is about to fail in a “red light” warning and another player who is holding him tight until he dies is similar to the situation that Ethereum is in now and there is a lot of hope that the network will finally be freed from its problems.
In this article, with help an article It is written from the Medium website, we intend to examine the reasons for the failure of Ethereum 1.0 and the reasons for the salvation of Ethereum 2.0 from the point of view of Ehsan Yazdanparast; So stay with us until the end of the article.
Why did the first version of Ethereum fail?
Let’s not kid ourselves about Ethereum failing. The truth is that one of the main advantages of the Ethereum blockchain is its leadership in this field. In 2015, when Ethereum was born, the cryptocurrency market was still in its infancy. At that time, Ethereum competitors such as Polkadot, Solana, Algorand and Cosmos did not exist at all; For this reason, Ethereum met with an impressive initial adoption. In fact, Ethereum’s network effect that attracted users and audiences helped its parent token, Ether (ETH), grow exponentially.
Read more: What is Ethereum? Shopping training and wallets
However, as time passed and as new projects and blockchains entered the market, the problems of the Ethereum blockchain became more apparent. Let’s take a look at these problems.
First problem: Proof of work consensus algorithm
If you review the basics of blockchain networks, you will notice that one of the important features of blockchain is its “consensus mechanism”. By definition, “a consensus mechanism refers to any number of methods used to achieve agreement and trust and security in a decentralized computer network”.
Each blockchain consists of hundreds of thousands of members. Thousands to millions of transactions are done in such networks. Also, all members of the network must agree on certain terms and rules to verify and authenticate and secure all transactions. Achieving such an agreement is only possible with “consensus mechanisms”. Some popular consensus algorithms are:
- Proof of Activity Algorithm: Active stakeholders are rewarded for maintaining a full node and configuring it to sign transactions. This consensus algorithm is a combination of proof-of-work mechanism and proof-of-stake mechanism.
- Proof of Authority Algorithm: Proof of Validity is the consensus mechanism used in private blockchains that validates the private key to generate all blocks or verify transactions.
- Proof of Burn: Miners send digital currencies to an inactive address and, in effect, burn them. The burned digital currencies are then recorded on the blockchain and the user is rewarded for them.
- Proof of Capacity: Proof of capacity for plotting or recording Plot file The hard drive points. This process means saving the answers or possible solutions to the problem on the hard disk before starting the extraction process. Finally, the hard disk with the fastest solution will receive the block reward.
- Proof-of-Developer: Proof of Developer (POD) is a type of digital credential that can be used to verify the identity and authenticity of a platform developer. Employers can use this algorithm to verify the developer’s identity and qualification. Also, developers use it to prove their skills and experience to employers.
- Proof of charity (Proof-of-Donation): This algorithm focuses on charitable donations through the blockchain network. In other words, the smart contract is responsible for directing the funds to the wallets of one of the charity organizations.
- Proof of Elapsed Time: It is a consensus algorithm in which nodes must wait for a randomly determined period of time. The first node to complete this time period will be rewarded.
- Proof-of-Liquidity: In the proof of liquidity algorithm, having specific amounts of liquidity of each actor in the network must be verified by a third party and signed and encrypted.
- Proof-of-Replication: In this algorithm, which is commonly used in connection with the Filecoin network and data storage networks, the miner proves to the network that he has stored a completely unique copy of a piece of data in his storage location.
Read more: Coin file review; The most complex project in the blockchain industry!
- Proof-of-Spacetime: In this algorithm, it is guaranteed that a certain amount of space is used for storage.
- Proof-of-stake: A consensus mechanism in which a person or “verifier” validates transactions or blocks.
- Proof-of-Work: It is a consensus mechanism in which a group of people or nodes mine each block in the network.
The current version of Ethereum and Bitcoin both use proof of work as their consensus mechanism. In fact, both are considered old blockchains, and in the past, proof-of-work was the dominant consensus mechanism in networks. After some time, it became clear that the proof-of-work consensus algorithm has many problems; Including:
- Expensive extraction
- Vulnerability against 51% attacks
- Harms related to the environment
- High transaction fees
These days, most blockchains, including Ethereum’s competitors, use more advanced and optimized consensus mechanisms like the ones we mentioned earlier. Therefore, the proof-of-work algorithm in Ethereum is considered a big problem in this blockchain.
The second problem: transaction fees
Ethereum platform and blockchain network is based on smart contract and users can use the main token of this network for various purposes; For example:
- Make payments.
- Move Ether between different wallets.
- Exchange Ether for other ERC20 tokens.
- Buy NFTs.
- to play
- Use it in DeFi protocols (decentralized financial affairs).
Users must pay transaction fees for all the above purposes and regardless of which application they are involved with. The transaction fee is considered as an incentive for the nodes that are responsible for checking and verifying the transactions in the network.
Read more: What is DeFi or decentralized finance?
With the growth of the network and the introduction of decentralized applications and more use of the network, the Ethereum blockchain has become more and more crowded, and this congestion means more fees for transactions in this network. The more expensive fees are mainly because in this case, there will be more competitors to verify transactions. In fact, the network, like a bank, consists of miners or nodes and a large number of clients (Blockchain users). The more requests banks receive, the longer they take to process and may increase their processing fees.
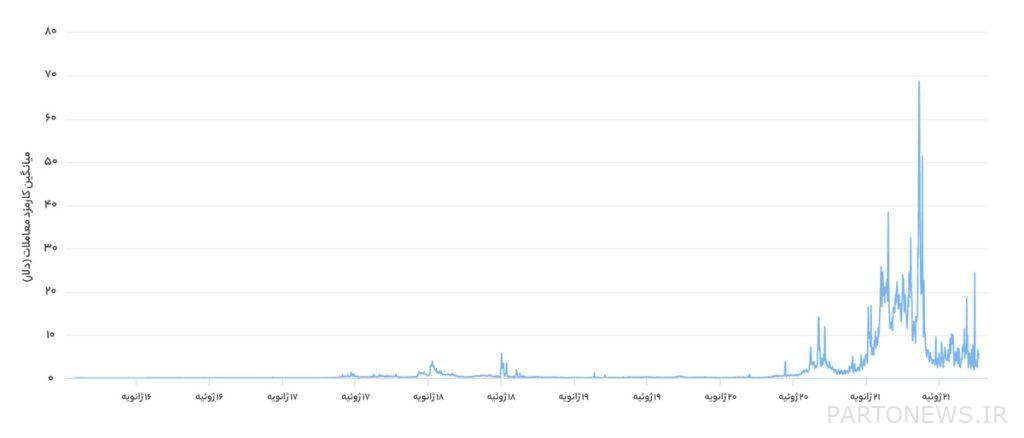
If you check the chart above, you can see that on some days, the average transaction fee is around $80. This cost is really staggering! High transaction fees may not be a problem for rich people trading NFTs or whales trying to transfer or exchange their tokens; But paying tens of dollars in fees for small and medium investors is a troublesome issue.
The third problem: effects of inflation and scarcity
According to CoinMarketCap’s definition, the maximum supply of a digital currency is the maximum number of which that digital currency will eventually exist. Next, we have brought the maximum supply of some famous currencies:
Bitcoin (BTC): 21 million units
Cardano (ADA): 45 billion units
Binance Coin (BNB): 168 million 137 thousand 36 units
Ripple (XRP): 100 billion units
Uniswap (UNI): 1 billion units
Olench (AVAX): 720 million units
Litecoin (LTC): 84 million units
China Link (LINK): 1 billion units
ALGO: 10 billion units
Bitcoin Cash (BCH): 21 million units
Poligan (MATIC): 10 billion units
However, Ethereum (ETH) does not have a supply cap. This means that there is no limit to the issuance of new Ether tokens; Therefore, this is also one of the problems of this protocol. Think fiat currencies. Governments print completely unbacked currency to pay debts or expenses or salaries, causing inflation. In the short term, more money may solve problems; But in the long run, more money equals more inflation, and more inflation equals more chaos.
Ether is not produced like fiat money; But there is no limit for issuing new tokens. All of this means that as we move forward, this inflationary effect will cause problems for the network. Another factor is the scarcity of digital currency. One of the main reasons for Bitcoin’s popularity is that it is considered a scarce asset. We will eventually have 21 million units of it and it will take until 2140 to supply all 21 million units. This issue strongly affects supply and demand. If an asset is scarce, demand for it will increase over time with limited supply in the market; But unlike Bitcoin, the current Ether is inflationary and not scarce.
Why is the second version of Ethereum the savior of this network?
According to the Ethereum Foundation, “Ethereum 2.0 applies a series of continuous updates to the network that make Ethereum more scalable, secure, and stable.” These updates are provided by multiple teams across the Ethereum ecosystem. In summary, Ethereum 2.0 will implement Proof of Stake (PoS) in Ethereum and Proof of Stake will also help keep Ethereum more secure.

Look at Ethereum 2.0 as a change that will make Ethereum healthier and give you more Ether in the process. In practice, in this update, you stake Ether to activate the validation software, and at the validator position, you process transactions and create new blocks in the chain. Another important point is that the staking and accreditation process is simpler than the current mining model. It is hoped that this upgrade to the network will help make Ethereum more secure in the long run. The more people are members of the network, the more decentralized and secure the network becomes. Overall, the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism leads to greater security in the network.
Also, Ethereum 2.0 improves transaction cost and processing time issues by introducing sharding mechanisms. With this upgrade, the said platform will perform thousands of transactions in a shorter time. Sharding is an important part of this upgrade. In simple language, sharding means separating and dividing a large chain into smaller chains (shards). After this upgrade, the workload between multiple validator distribution and sharding will lead to greater scalability, lower transaction fees, and faster transaction processing speed.
Read more: What is sharding? A way to improve scalability
The introduction of Ethereum 2.0 turns Ether into a profit-generating asset; Therefore, it can be expected that the number of active network nodes will grow exponentially. In addition, the introduction of the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm and the sharding mechanism and new approaches related to validation activities completely revolutionize the Ethereum 2.0 blockchain. These, along with the introduction of features like EIP-1559, make Ether a rare and non-inflationary asset in the future. Not to mention, Ethereum’s second-layer scaling solutions enhance the performance of Ethereum 2.0 by improving the following:
✔️ Increase Ethereum throughput (number of transactions per second)
✔️ Reducing confirmation latency (the amount of time it takes for a transaction to be confirmed)
✔️ Reduction of transaction fee (Gas)
✔️ Ensuring a lot of security by relying on the security of the Ethereum blockchain
For example, in terms of transactions, the current Ethereum blockchain can handle 15 to 45 transactions per second. Meanwhile, scalable solutions of the second layer have increased this number to 1,000 to 4,000 transactions per second. Combined with the introduction of Ethereum 2.0, the Ethereum blockchain is expected to process around 100,000 transactions per second. Also, increasing the number of transactions per second means less congestion in the network, and this will likely reduce transaction fees in the network.
Conclusion
Ethereum’s history is mixed with significant successes and failures. Now the most important and fateful change of Ethereum is about to happen. This change, known as Ethereum 2.0, is supposed to make Ethereum a better performing network. The most important change of Ethereum 2.0 compared to Ethereum 1.0 is the change from Proof of Work (PoW) model to Proof of Stake (PoW) with the aim of improving the security and scalability of this network.
It can be said that Ethereum 2.0 is a step in the right direction. Indeed, this update, achieved after years of hard and continuous work, is a testament to the purposefulness and responsibility of the Ethereum team. This upgrade could strengthen Ethereum’s foundations in the cryptocurrency market and be the true savior of the network.

