Symptoms and the best treatment of osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a silent disease that silently weakens your bones over the years, making you more prone to fractures. Do you know what are the symptoms of osteoporosis? What is the best treatment for osteoporosis? Does this disease have a definite cure? In this article we will answer all these questions.
What we read in this article
What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a disease that weakens the bones; It means that despite this disease, the density of your bones decreases. The possibility of bone fractures is very high in people with osteoporosis. In healthy people, bones are constantly breaking down and rebuilding. But in osteoporosis, the rate of bone breakdown is higher than the rate of regeneration. This causes the bones to become weak and brittle.
Unfortunately, most people notice their osteoporosis when they have a bone fracture. Osteoporosis is especially common in postmenopausal women. Due to osteoporosis, bones in any part of the body may break, but the most likely to break are these bones:
- pelvis
- wrist
- spinal cord
The sooner osteoporosis is treated, the less likely it is to break bones. Buying bone and joint pills is one of the best ways to prevent and treat osteoporosis.
How common is osteoporosis in Iran?
Statistics show that two-thirds of women over 60 in Iran have osteoporosis. At the age of 75, this figure reaches 80%. In general, osteoporosis is more common in people over 50 years of age. Scientists estimate that half of women over the age of 50 and one in four men after age 50 suffer from osteoporosis.
Also, studies show that 1 out of every 3 people over 50 years of age who do not suffer from osteoporosis have some degree of bone density reduction or osteopenia. People with osteopenia have early symptoms of osteoporosis, and if they are not treated, they have a 100% chance of developing osteoporosis.
What are the symptoms of osteoporosis?
Like many other diseases, osteoporosis is also a silent disease. In fact, despite this disease, you will not have any symptoms to notice this disease. This means that there will be no symptoms such as fever, headache or stomach ache. The most common symptoms of osteoporosis are bone fractures, which actually happen when a person has had osteoporosis for a long time but is unaware of it. Warning signs of osteoporosis are as follows:
- Loss of 1 inch of height (about 2.5 to 3 cm)
- A change in the body’s natural posture (for example, leaning forward more)
- Shortness of breath (if the discs in your spine are compressed enough to reduce your lung capacity.)
- back pain (spine pain)
Cause of osteoporosis
Before treating osteoporosis, we must first examine its cause. Osteoporosis occurs when bones lose their ability to regenerate and repair due to aging. Bone, like other parts of the body, is a living tissue that repairs itself many times throughout life. That is, cells and bone tissue are constantly being replaced.
By about age 30, your body naturally makes more bone than it loses. But after the age of 35, bones break down faster than the body can replace them. In this case, the density of the bone mass gradually decreases. If you have osteoporosis, it means that you are rapidly losing bone density. In women, bone loss peaks after menopause. Fortunately, there are ways to treat osteoporosis.
Effective factors in osteoporosis
Anyone can develop osteoporosis, but the possibility of osteoporosis increases in the following cases:
- Menopause (due to hormonal changes)
- genetic background
- Taking some medications
- Calcium and vitamin D deficiency
- Not having enough physical activity
- Smoking and drinking alcohol
- Age over 50 years
- thin people
Health conditions influencing osteoporosis
Some health conditions increase the risk of osteoporosis:
- Endocrine disorders (any condition that affects your thyroid, parathyroid, or hormones)
- Gastrointestinal diseases (such as celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease)
- Autoimmune disorders that affect the bones, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Blood disorders such as leukemia
Drugs or surgeries affecting osteoporosis
- Diuretics (medicines that lower blood pressure and remove too much fluid from the body.)
- Corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Seizure drugs
- Slimming surgeries for weight loss
- Hormone therapy for cancer (especially breast and prostate cancer)
- Anticoagulants
- Proton pump inhibitors (Medications that treat gastric reflux may decrease the body’s absorption of calcium.)
Important note: Be careful that not getting enough calcium and vitamin D from the diet and lack of physical activity are the most important causes of osteoporosis.
If you have a calcium deficiency, be sure to use calcium tablets in addition to correcting your diet with the doctor’s advice. Vitamin D deficiency is very common in Iranians. With a blood test, make sure that you are not deficient in this vitamin in your body. If necessary, buy vitamin D tablets after consulting your doctor. But how is the treatment of osteoporosis?
Treatment of osteoporosis
The most important part of treating osteoporosis is preventing bone fractures. To treat osteoporosis, doctors usually recommend a combination of treatments to slow bone loss and strengthen bone tissue. Osteoporosis treatment is a combination of the following:
Calcium tablets and vitamin D tablets to treat osteoporosis
Calcium and vitamin D3 tablets are usually prescribed for people with osteoporosis. According to each person’s condition, the doctor determines how many times a day to take these supplements and what the exact dosage should be. You may also be prescribed cartilage-building pills to improve joint health.
Exercise to treat osteoporosis
Regular exercise can strengthen your bones and the tissues attached to them, such as tendons, ligaments, and muscles. Exercises such as walking, yoga, pilates, and tai chi can improve your strength and balance without putting stress on your bones. In cases of severe osteoporosis, specific exercises should be recommended by a physiotherapist.
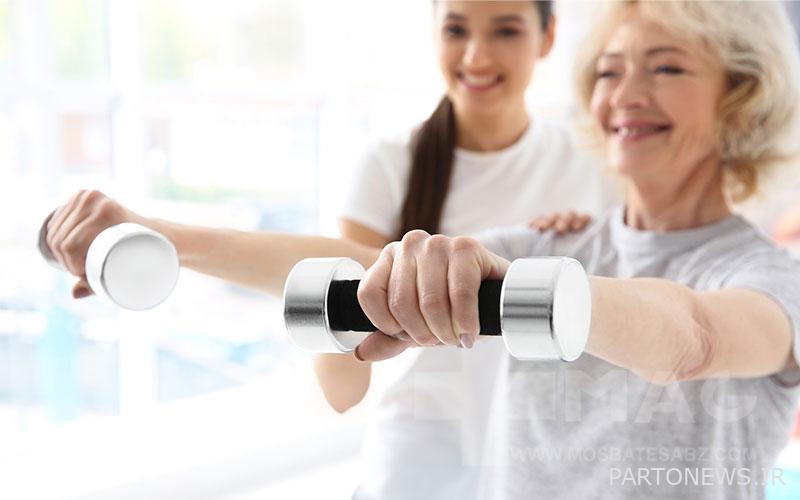

Weight bearing exercises such as walking or running are very suitable for osteoporosis. Also, weight lifting and lifting light to moderate weights are sometimes suggested for the treatment of osteoporosis.
If you are suffering from osteoporosis, be sure to consult your doctor before trying to exercise because any type of exercise may not be suitable for your condition.
Medicines to treat osteoporosis
The most common medications prescribed to treat osteoporosis include:
- Hormonal treatments (including estrogen or testosterone replacement and bisphosphonates)
- Medicines including parathyroid hormone (PTH) analogs, denosumab, and romosuzumab (for people who are at high risk of breaking bones due to osteoporosis.)
Some of this medicine may be administered by injection.
Read more: What medicine is good for osteoporosis?
What to eat for osteoporosis?
Diet is very important in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. The following foods are recommended for bone health:
- Foods rich in calcium such as milk and dairy products, green leafy vegetables, salmon, broccoli and legumes such as beans.
- Foods rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish such as salmon and sardines, eggs, vitamin D-fortified milk, and breakfast cereals.
- Foods rich in protein such as: meat, fish, eggs, beans, nuts

Treatment of osteoporosis in traditional medicine
In traditional medicine, there are solutions for the treatment of osteoporosis. Some medicinal plants that are recommended in traditional medicine for the treatment of osteoporosis are:
- Nettle: Nettle contains high levels of calcium, magnesium and vitamin K, which are beneficial for bone health. Note that magnesium and vitamin K deficiency also play a role in the occurrence of osteoporosis.
- Ginkgo biloba: Ginkgo biloba helps improve blood circulation in the bones.
- Turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin and helps reduce inflammation and pain caused by osteoporosis.
- Elderberry: Elderberry contains high amounts of calcium and vitamin C, which are beneficial for bone health.
- Ginger: anti-inflammatory, has antioxidant properties and improves inflammation caused by osteoporosis and arthritis.
Ways to prevent osteoporosis
In the previous episode, we talked about the treatment of osteoporosis. But prevention is always better than cure. Regular exercise and making sure you always get enough calcium and vitamin D in your diet are the most important factors in preventing osteoporosis. Also, quitting smoking and alcohol is also effective in preventing this disease.
Diagnosis of osteoporosis
To treat osteoporosis, you must first make sure that you have this disease or not. Osteoporosis is usually diagnosed with a bone density scan. This scan measures the amount of calcium and other minerals in the bones.
There are two main types of bone density scans:
- DXA: This type of scan is the most common type of bone density scan. In this scan of X-Ray It is used with a low level to measure bone density in the spine, pelvis, or wrist. This is an outpatient procedure.
- Bone sampling: This is a slightly more invasive procedure and uses a needle to remove a small sample of bone. This sample is then examined in the laboratory to measure bone density.
Bone density scan results are reported based on a scale called T-score. T-score shows how different your bone density is from the bone density of a young, healthy person.
A T-score below minus 2.5 indicates osteoporosis. A T score between minus 1 and minus 2.5 indicates osteopenia, which is a pre-osteoporosis condition and puts a person at risk of developing this disease.
A final word about the treatment of osteoporosis
We said that the symptoms of osteoporosis usually occur when a bone fracture has occurred. Otherwise, this disease is a silent disease that may exist for years but the person is unaware of it. For the treatment of osteoporosis, exercise is usually recommended along with taking bone and joint pills. If you suspect that you have osteoporosis, be sure to see an orthopedic doctor for specialized examinations.

