The beginning of a new phase of liquidity growth control with banking network discipline

According to the report of Iran Economist, the rapid growth of liquidity has been one of the most important factors of rampant inflation in the country’s economy in recent years. Accordingly, the 13th government and the Central Bank in particular made reducing the speed of liquidity growth one of the priorities of their monetary policies.
The Central Bank of the Thirteenth Government targeted the main source of unaccounted growth and liquidity, i.e. the banking system, by limiting the growth of the balance sheets of the country’s banks since the beginning of its work in the middle of last year. Based on this policy, the central bank established a 2% monthly growth limit for commercial banks and a 2.5% monthly growth limit for specialized banks.
A significant decrease in the acceleration of liquidity growth in the 13th government
A look at various statistics related to the money market and liquidity shows that the central bank has been successful in implementing this policy and reducing the acceleration of liquidity growth in the new period. As an example, the examination of the balance of bank network facilities, which is a very important factor in creating liquidity, shows the success of the central bank’s policy in controlling the growth of banks’ balance sheets and, as a result, reducing the acceleration of liquidity growth.
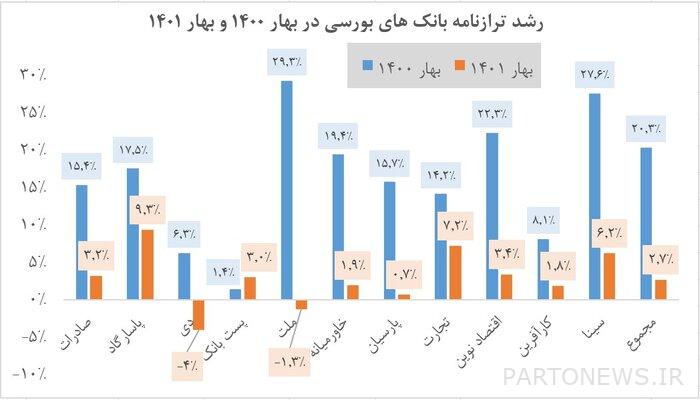
Reviewing the monthly activity report of stock-exchange banks shows that the growth of stock-exchange banks’ facility balances has increased in the spring of this year at a much lower rate than in the spring of last year. This change is shown in the diagram below.
As can be seen, the monthly growth of stock exchange bank facilities during the first three months of this year is far less than the first three months of last year. The decrease in the growth of banks’ facilities, which is an important factor in the growth of liquidity in the country, shows the positive effect of the central bank’s policy in reducing the acceleration of liquidity growth. It is necessary to explain that the reason for not reviewing the balance sheets of non-stock banks was the unavailability of their information.
In addition, according to the new statistics of the central bank, the growth of liquidity in April has reached minus 0.2%, which indicates a decrease in the volume of liquidity in this month. The decrease in the volume of liquidity in the situation where the country has experienced a liquidity growth of over 30 and even 40 percent in recent years is a promising sign of the positive effect of the policies of the central bank. Despite this positive trend, the Central Bank is not satisfied with these policies and has adopted a new policy to improve the management of the country’s monetary system.
The central bank’s strictness on the growth of weak banks’ balance sheets
According to the announcement of the head of the central bank, the policy of the central bank to control the growth of liquidity by limiting the growth of the banks’ balance sheets has entered another phase. Based on this, the policy of limiting the growth of the banks’ balance sheets will apply more strictness on the growth of the balance sheets of the weak banks by dividing the country’s banks into weak and strong categories in terms of capital adequacy.
The head of the central bank said about the control of the growth of banks’ balance sheets and the bank’s disciplinary programs: the growth of banks’ balance sheets is considered to be from 1.5 to 2.5 percent. Accordingly, for some banks, 1.5% and 2.5% have been considered for banks, depending on the conditions of that bank and the available indicators.
Ali Salehabadi emphasized: A bank that does not comply with this requirement will be subject to a higher legal deposit, and we have had cases where their legal deposit can be increased up to 13%.
According to Iran Economist, changing the direction of the money creation machine of banks by focusing on undisciplined and weak banks in terms of capital adequacy, while continuing and even improving the control of liquidity growth, will lead to the reform of the banking system and more discipline of banks in asset and debt management.