What are Inflation Assets and Anti-Inflation Assets?

In recent years, economic crises have made people more or less familiar with the concept of inflation. Different definitions have been proposed for this economic phenomenon; But some of them are not so logical. Undoubtedly, all people have felt the impact of inflation on their lives. The inflation we are talking about has happened to the economies of different countries, and we can say that many national currencies have been involved in this phenomenon in some way.
What does inflation have to do with the national currencies of countries? In response, we must say that people usually interpret inflation in the form of rising prices for goods and services; But in reality, inflation is equivalent to devaluing money and reducing purchasing power by a certain amount of money per unit time.
Inflation can have many complex causes, and there are several ways to control it in the economy. However, one of the factors influencing inflation is the type of asset we are dealing with. In fact, the nature of some assets «Inflation»And the nature of some others«Anti-inflation” Is.
In this article, we are going to give a definition of inflation and anti-inflation assets by looking at the money supply method, and then introduce some examples of traditional and digital assets. At the end of this article, you will gain a deeper understanding of inflation and its root cause, and the importance of knowing the supply ceiling of your assets. So stay tuned.
What are Inflation Assets and Anti-Inflation Assets?
In general, inflation, as an important concept in economics, is directly related to money supply. To better understand these concepts, let’s compare bitcoins and fiat currencies.
If you are a little familiar with bitcoin, you know that the total supply ceiling of this digital asset is 21 million units; This means that the number of available bitcoins will never exceed this amount. So far, about 19 million units of this digital asset have been extracted, and no extra bitcoins will be produced after extracting another 2 million units.
Read more: What is inflation?
In contrast, the flow of Fiat currencies, like the dollar, is a bit more complicated. There is no supply ceiling for these assets, and the amount of money in people’s hands is determined solely by central bank policies. In the meantime, only the central bank is allowed to collect and destroy new printed money or old and defective money. Therefore, central banks are responsible for planning the decline or increase of Fiat currencies in times of financial crisis and have complete control over bank interest rates.
The relationship between interest rates and inflation is one of the topics on which there are various perspectives. Economists believe that by lowering bank interest rates, more money will flow into society, which could have a significant impact on the inflation of national currencies. Of course, this is the opposite from the point of view of some experts, and they consider the increase in bank rates to increase inflation.
Now that we know the definition of money supply, we can easily identify inflationary and anti-inflationary assets. If we take this simple assumption that the less scarce an asset is, the more valuable it is, the more money it means, the more worthless the money becomes and the less purchasing power people have.
Because the central bank can print new money at any time and there are no restrictions on money production, the value of national currencies, such as the dollar and the euro, declines over time. For example, if the price of a commodity is $ 1 in 2020, $ 1.5 in 2021, and $ 2 in 2022, then the cost of that commodity has not increased; Rather, the value and position of money is in a downward trend. The main reason for the devaluation of the Fiat currency is the increase in its printing by the central bank; This is an issue that reduces the amount of money that is scarce over time.
In general, inflation is caused by an increase in the money supply and a decrease in purchasing power.
Central banks do not prevent the printing of money; Therefore, all major Fiat currencies today are considered inflationary, and all the hypotheses and theories put forward in economics are based on an inflation model.
In contrast, deflationary conditions arise when purchasing power increases and, as a result, the price of goods and services decreases over time. The important thing about Bitcoin is that there is no central bank that constantly prints money and adopts fiscal policies.
In fact, the bitcoin supply process ends when it reaches 21 million units. After that, any bitcoins that are lost or unavailable will, in effect, be permanently removed from the coins. In other words, over time, total supply decreases and this digital currency becomes more scarce and more valuable.
The most obvious Examples of Inflation Assets
We introduced bitcoin against Fiat currencies as an anti-inflation asset; But we can not say that all digital assets are anti-inflationary. Both in the world of digital currencies and in the traditional economy, we are dealing with various inflationary assets, which we describe below.
Non-crypto example: Fiat money
The word “fiat” is a Latin word meaning “should be” or “let it be done”. In fact, Fiat currencies are valuable only because governments maintain their value. In the past, governments minted coins from valuable physical goods such as gold or silver. This asset could be redeemed for a certain amount of physical goods. However, Fiat currency is non-refundable and cannot be redeemed simply because it has no backing.
Because Fiat money is not dependent on physical reserves such as gold or silver, it is at high risk of losing value in the event of hyperinflation. In events like what happened in Hungary after World War II, inflation may double in one day. Such conditions are considered hypertrophy.
Read more: What is Fiat Currency?
In addition, public confidence is an important factor in the growth or decline of the fiat currency position of countries. This is very different from a currency backed by gold. The demand for gold in jewelry and the manufacture of electronic devices, computers and aircraft is enormous; Therefore, this makes the gold-backed currency more valuable.
Cryptographic example: Unrestricted currencies such as Polkadat
As mentioned in the Money Supply section, any asset that does not have a limited supply is likely to be among the inflation assets. Many digital currencies, such as DOT, have no supply limits. The Polkadat network has not set a ceiling for the supply of .ot, and this rate is facing an inflation rate of about 10% per year.
In the meantime, we should also mention that the digital currency inflation policies of Dot have been set with the aim of encouraging users to share and use network assets. So far, more than 1.1 billion dot-coms have been released, of which about 987 million are in circulation and the rest have been burned in a specific process.
The most obvious Examples of anti-inflation assets
Although it seems that only in the crypto world we see anti-inflationary assets, we must pay attention to the fact that in the traditional market there are also non-inflationary assets.
Also read: What is negative inflation and what effects does it have on the economy?
Non-crypto example: gold
Gold has been a treasure trove for centuries because of its scarcity. No individual or group can create gold. In fact, the supply of gold is controlled by nature and has a very limited amount. Gold is a rare and widely used metal in the electronics and medical industries; Thus, it is obvious that high demand versus low supply makes this asset more valuable.
Gold is often used as an anti-inflationary cover for Fiat currencies; Because, as you can see in the diagram below, the supply of this precious metal has an almost constant inflation rate.
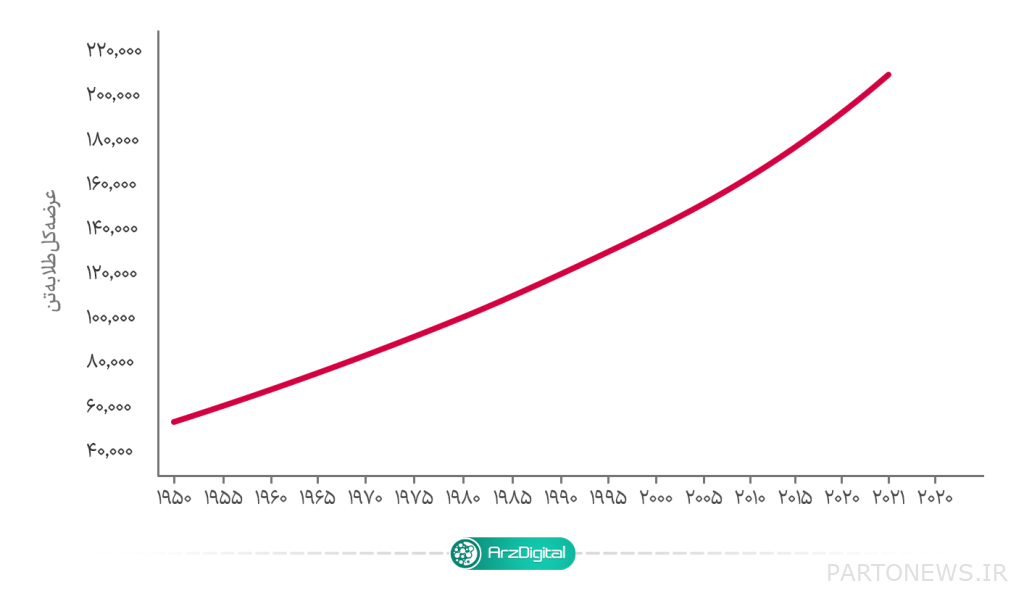
Cryptographic example: Bitcoin
It is interesting to know that the creators of Bitcoin also designed its inflation rate in a way that mimics the stable inflation rate of gold. The chart below shows the circulation of bitcoin since 2009.
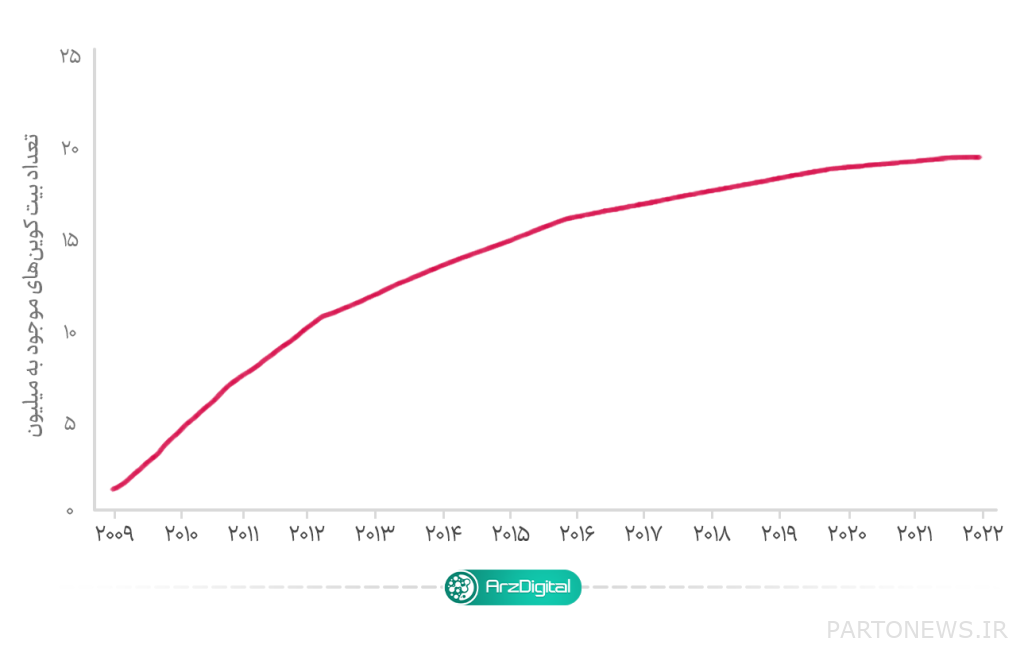
Under constant conditions, as the inflation rate decreases, the price of each bitcoin should increase. Bitcoin inflation rate is included in its software coding. Finally, the Bitcoin inflation algorithm is supposed to turn this digital currency into a scarce and valuable asset.
In fact, bitcoin, like other reserves of value, is scarce and popular, and counts as an anti-inflation asset. goes. Overall, the anti-inflationary nature of bitcoin depends on two main rules:
- In total, only 21 million bitcoins can be produced and supplied.
- In an event called Halving, which occurs every four years, the bitcoin supply is halved.

In addition, users’ willingness to invest and store bitcoins increases the value of this digital asset. As we have mentioned, at present, about 19 million bitcoins have been mined and some of them have been destroyed for various reasons and are no longer available. This makes this asset scarce and its anti-inflationary feature more prominent.
According to calculations, Hawing events will reduce bitcoin supply to zero by 2140. Suffice it to say that 19 million units of bitcoins have been released over the life of this asset for about 13 years, and the remaining 20 million units are expected to be released over the next 120 years! This gradual supply also increases the value of this digital asset.
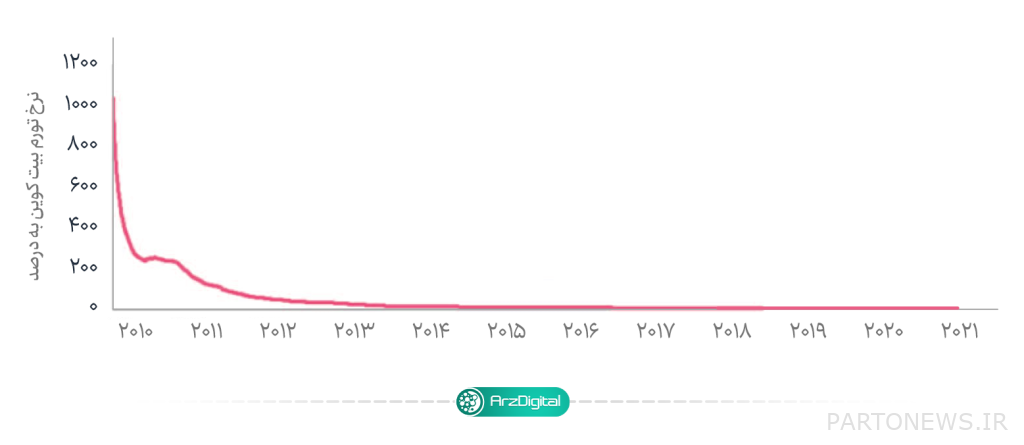
Conclusion
It is called the devaluation of money and the purchasing power of inflation. This often happens because of the outflow of money. In contrast, anti-inflationary conditions are defined by the scarcity and value of each asset. In this article, we explained that different assets may be inflationary or anti-inflationary, depending on the support and policies they pursue to increase or decrease supply.
Inflationary and anti-inflationary assets are found in both digital and traditional currency markets. For example, in addition to Fiat currencies, some digital currencies, such as Pulkadat, also fall into the category of inflationary assets. Instead, assets such as gold and bitcoin are considered anti-inflationary because of the way they are offered, and their value increases over time.

