What is lupus disease? Symptoms and treatment methods
Lupus is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks healthy tissues and causes adverse effects. Do you know that women are 9 times more likely to get lupus than men? In this article, we will examine the cause, symptoms and treatment of lupus.
What is lupus disease?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can cause swelling, inflammation, and pain. In autoimmune diseases, the body’s immune system starts fighting the body itself. The immune system should naturally deal with possible threats to the body such as infection, but in lupus, it mistakenly goes to healthy body tissue. People with lupus may experience skin rashes, joint pain, and problems with internal organs such as the brain, lungs, kidneys, and heart.
Many of these complications may appear periodically and disappear after a while. In some people, the symptoms of lupus may be mild and not noticeable at all. But some people may experience severe symptoms that have a negative impact on daily life.
Types of lupus
There are different types of lupus, among which systemic lupus erythematosus is more common than others. Other types of lupus include:
- Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: affects the skin. Sun sensitivity and pustular rash are symptoms of this disease. People with cutaneous lupus erythematosus may also experience hair loss.
- Drug-induced lupus: This disease is caused by the use of certain drugs. The symptoms of this disease are usually similar to the previous type, but they are temporary and disappear when the drug is discontinued.
- Neonatal Lupus: It is a rare type of Lupus that is seen in some babies at birth. Children born with neonatal lupus have antibodies passed down from their mothers. Be careful that every baby born to a mother with lupus does not necessarily mean that he will be affected by this disease.
What is the cause of lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune disease, but its exact cause seems unclear. The immune system is a complex network consisting of organs, tissues and cells. This system protects the body against external factors such as toxins, viruses, bacteria and fungi. The immune system takes care of the body by producing Y-shaped proteins called antibodies. These antibodies either neutralize the foreign agent or send a signal to other cells to remove it.
Antibodies are produced by white blood cells. When a person has an autoimmune disease such as lupus, the immune system cannot distinguish between antigens and healthy tissue. So the body mistakenly considers itself as an external factor. As a result, the immune system directs antibodies against healthy tissue and antigens and causes factors such as swelling, pain and tissue damage.
What factors increase the likelihood of lupus?
Lupus disease may develop in response to several factors. These factors include:
Hormones
Hormones are chemicals produced by the body. They control and regulate the activity of certain cells and organs. Women aged 15 to 44 are 9 times more likely to develop lupus than men. In 20% of cases, the symptoms of lupus may appear even after the age of 50. Estrogen, which is considered a female sex hormone, may be effective in lupus.
Many women experience lupus symptoms more before menstruation and during pregnancy because the level of the hormone estrogen in the body increases. There is more research on the role of hormones in lupus.
The influence of genetics in lupus
Scientists have identified certain genes that play a role in the immune system’s response and may also be effective in lupus. Evidence shows that if one family member has lupus, it is more likely that someone else in the family will also develop the disease.
Studies on identical twins show that if one of them has lupus, there is a 24% chance that the other will also get it.
Lupus may occur in people with no family history, but other autoimmune diseases are common in these people. White women have a lower risk of developing lupus than other races. More research is needed on the role of genetics in lupus.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors such as chemicals or viruses may play a role in the development of lupus in people who are genetically predisposed to lupus. Possible environmental triggers include:
- Smoking: Exposure to toxic components of cigarette smoke may lead to genetic mutations and gene activation associated with SLE (lupus).
- Exposure to sunlight: Direct sunlight can worsen the symptoms of lupus that a person already has. UV rays can lead to cell damage and genetic mutations that may play a role in lupus.
- Infections: Infections such as Epstein-Barr virus, also known as glandular fever, are much more common in people with SLE.
- Pollutants: Pollutants such as cigarette smoke or air pollution may contribute to lupus.

Do children get lupus?
Lupus can occur at any age. 20% of people with lupus develop this disease before the age of 20. It is rare for people to develop lupus before the age of 5. Lupus that develops in childhood has more severe symptoms and often affects the kidneys; So that up to 50% of children with lupus have kidney problems.
Lupus symptoms
Related posts
Lupus symptoms appear when the disease flares up. Other times there are fewer symptoms. The most important symptoms of lupus are:
- tiredness
- Muscle and joint pain
- Fever
- Chest pain when breathing deeply
- Sensitivity to sunlight
- Ulcers in the mouth
- Memory problems
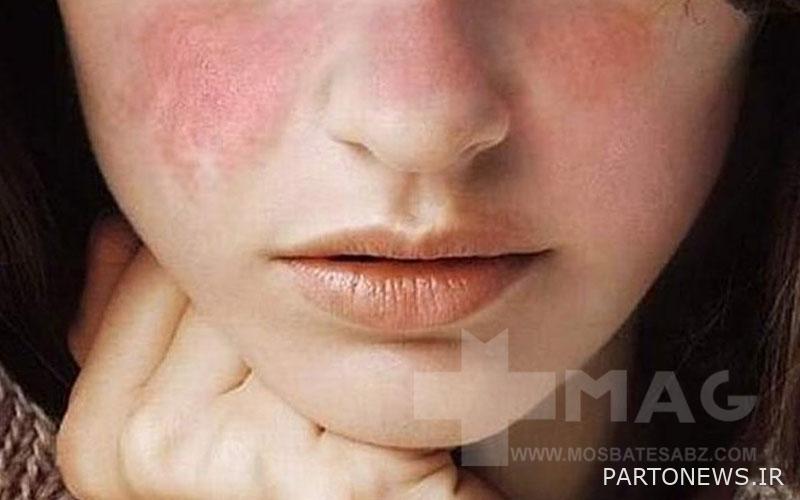
- Malar rash (red, butterfly-shaped rash all over the nose and cheeks)
- Headache
- Abnormal hair loss
- Pale or bruised fingers and toes due to cold or stress
- Arthritis
Lupus symptoms in women
Women usually have more severe symptoms than men. These symptoms include:
- hair loss
- Sensitivity to sunlight
- Ulcers in the mouth
- Arthritis
- Malar rash
Lupus symptoms in men
It’s not just women who can get lupus. The risk of men getting this disease is lower. Lupus symptoms in men include:
- Cardiovascular complications
- You are low blooded
- Weight Loss
- Kidney complications
- Chest pain
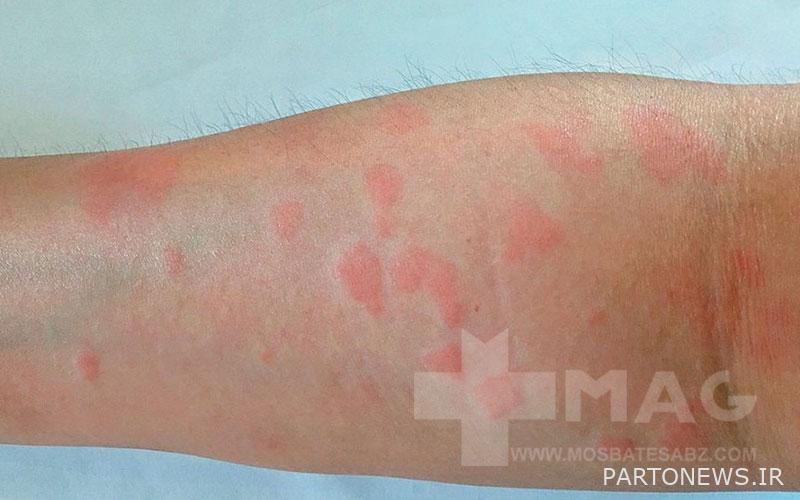
The impact of lupus on other body systems
Suffering from lupus can have a negative impact on these organs and their function:
- Kidney
- lung
- Central nervous system
- blood vessels
- Blood
- Heart
Treatment of lupus
The goal of treating lupus is to reduce inflammation to protect the organs and prevent the disease from escalating. Lupus treatment plan is considered different for each person depending on the type of disease and its severity. Treatment for lupus often includes:
- Hydroxychloroquine : It is an antimalarial drug that treats rashes and arthritis symptoms in lupus.
- Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants: These can include high-dose corticosteroids, such as prednisone, and drugs that suppress the immune system, such as mycophenolate and methotrexate. The goal of this treatment is to control inflammation.
- Blimumab is a biologic agent approved by the FDA for the treatment of lupus.
A doctor may prescribe medications to treat complications that develop in people with lupus. Such as: seizure medications, antibiotics for infections, and vitamin D to help improve kidney function.
Home remedies for lupus
Some evidence suggests that diet can be effective in treating lupus in limited cases. Aim for a balanced and varied diet that includes fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and a moderate amount of protein. Some of the changes that a person with lupus can make in their diet include:
- Consumption of omega 3
- Consuming less unhealthy fats
- Consume less sodium (salt)
- More attention to vitamin D and B sources
Other changes in the lifestyle of people with lupus can be as follows:
- Avoid smoking
- No alcohol consumption
- Exercise
- stress management
43% of people with lupus are worried about social isolation. Therefore, it is better to be supported by family and friends.
Is lupus dangerous?
The severity of lupus can be mild to very severe. If a person with lupus is under medical care and takes preventive measures, they can recover and live a good life. Be careful that sometimes lupus can cause serious damage to the kidney and in this case it can lead to death.
The consequences of lupus
Not all people with lupus die from this disease. If lupus affects other organs, such as the kidneys, lungs, or heart, it can cause death. Lupus sufferers can easily continue their normal life routine by controlling their insurance.
Please rate this article
[مجموع: ۱ میانگین: ۵]


