Are you planning to borrow from Defai? 3 threats you need to know

Suppose you want to borrow $ 1,000 from Atrium or Bitcoin, but you do not intend to sell your digital currencies. Defy lending platforms are your solution. Using these platforms, you can provide your ethers or bitcoins as collateral to the platform in a very short period of time and receive the desired amount in the form of a loan. In this case, you have not sold your ethers and provided the money you need.
When we all hear the name Difai and the digital currency market, we all think of tens of thousands of profits and countless opportunities to earn so much. However, we must not forget that in the world of investment, anything that has a high profit has its own risks; Diffay lending platforms are no exception. If you want to learn more about borrowing from Diffay lending platforms, we suggest you read this article.
As you know, DeFi stands for “Decentralized Finance”. Decentralized finance is actually an ecosystem of blockchain-based applications that provide financial services similar to traditional banks, insurance brokers, and other financial intermediaries.
The difference between traditional financial services and decentralized applications is that these applications, or dapps, work independently and without intermediaries; Because the performance of each of these applications, instead of individuals, is based on one or more smart contracts. You also know that a smart contract is a special computer program that automatically executes certain operations if the predetermined conditions are met.
“Lending” is one of the traditional financial services that has been made possible in the world of digital currencies through these decentralized peer-to-peer applications.
The emergence of lending in the decentralized world of digital currencies was a great achievement that made these currencies very popular and caused a large amount of capital to enter the defa platforms; But as we mentioned in the previous sections, this achievement of decentralized finance, like any other new and emerging phenomenon, is not without risk and has its own potential risks.
Continue and help an article From the Quin Desk website, we will look at three examples of these hazards and introduce ways to prevent them.
3 major threats to defy lending platforms
Diffay lending platforms are, in fact, the decentralized version of the traditional banks we turn to for Fiat currency loans. Of course, there are fundamental differences between the two; But their meaning and nature are the same.
Digital currency investors, just like when they deposit money into their savings accounts to make a profit, can now lock their funds in defa platforms and use them to cash in on those platforms and receive regular profits.
The interest rates on some of these decentralized apps are much higher than the fees paid by traditional financial institutions; So for digital currency holders, they are a passive and attractive source of income.
But do not forget that before lending or borrowing any asset, you must consider the risks associated with it and be aware of them. In the following, we will introduce and review some of these risks.
Unstable losses (Impermanent Loss)
When you deposit your assets into a liquidity pool, one of the risks you may face is a risk called “volatile loss”.
Unstable losses occur when the price of locked-in assets in a liquidity pool changes after a deposit and an “unrealized loss” occurs. In other words, if the liquidity provider or the investor kept his assets in digital currency, he would not suffer this loss.
Asset prices fluctuate for two reasons, both of which are inextricably linked to the automated marketing system used in Diffie liquidity pools:
- Defai pools hold a certain proportion of assets in the pool. For example, an ether / link pool may keep the ratio of ether and link tokens in the pool to 1:50; This means that anyone who wants to provide liquidity to this pool must deposit ether and link tokens at a ratio of 1:50.
- Diffie pools rely on arbitrage traders to keep asset prices at current market value; For example, if the price of a link token in the market is $ 35 and the price in an ether / link platform pool is $ 34.5, arbitrage traders will detect this price difference and add more ethers to the pool to profit from this price difference. Receive links that are traded at a lower price than the market.
When arbitrage traders add another token to the pool to collect a cheap token, the token ratio changes. The liquidity pool also automatically raises the price of more tokens and decreases the price of smaller tokens to restore the balance of tokens; Arbitrage traders have the financial incentive to maintain the balance of the pool.
When the pool balance is restored, the value of the liquidity pool is often less than when the same assets were held on the lending platform. “This happened”Unstable losses” they say.
Here is a summary of the data in the chart above and the relationship between price changes and the percentage of losses:
1.25x price change = 0.6% loss
1.5x price change = 2% loss
1.75x price change = 3.8% loss
2x price change = 5.7% loss
3x price change = 13.4% loss
4x price change = 20% loss
5x price change = 25.5% loss
Under these protocols, some transaction fees are paid to liquidity providers in exchange for adding assets to the pool, which can offset unstable losses. Uni Swap, for example, receives a 0.3 percent commission on transactions that is distributed among liquidity providers.
Important Note: To reduce volatile losses, it is best to invest your cash in pools that hold less volatile assets (such as stable coins).
Unstable damage should not be a factor in scaring you away from the defense space and away from it; Rather, you should look at it as a predictable and measurable risk that you should consider before lending assets.
Fast loan attacks (Flash Loan Attack)
Flash loans are a type of unsecured lending for defaults. In the traditional centralized banking model, there are two types of loans:
- Unsecured loans: In this type of loan, due to the lack of loan amount (for example, ordinary loans), there is no need to provide collateral;
- Collateral loan: These loans have a higher amount and require collateral such as title deed, car and investment. Throughout the lending process, banks use tools such as credit scores and account reporting to assess customer credit.
Quick loans are a type of unsecured loan that uses smart contracts to reduce the risks in a traditional centralized banking system.
Quick loan has a simple meaning: the borrower can receive thousands of dollars of digital currency without providing any collateral; But the important thing is that in this type of loan, Funds must be repaid in the same transaction as they were sent (usually within seconds).
If the loan is not repaid, the lender can repay the transaction; As if no such transaction had taken place and no one had received such a loan; Due to the zero risk of issuing these types of loans, there is no limit to the amount of loans a person can take out. Also, since the whole process is decentralized, no one will ask you if you have a returned check or overdue installments.
Rapid lending attacks occur when a person uses these types of loans to borrow large sums of money and use them to manipulate the market or exploit vulnerable defensive protocols to their advantage.
The instant loan attack that recently targeted PancakeBunny is one of the latest examples of such attacks. Shortly afterwards, the profiteering aggregator platform made headlines in digital currency news.
During the attack, the price of the BUNNY token fell by 95%. The attackers did this by borrowing a large amount of BNB from the Pancake Swap Lending Protocol, manipulating the price of the sponsor in the lending pools and then dumping the sponsor in the open market, which eventually led to a fall in the price of the token. Just like the previous quick loan attacks, this time the thieves escaped without any problems.
When a particular token in a liquidity pool runs out of stock, liquidity suppliers may be exposed to volatile losses. It is clear that when lesser-known tokens (such as sponsors) are targeted, investors lose confidence in the projects. Also, the price of these tokens is rarely revived and returns to the previous price.
Rag Defy Money (Rug Pull)
First of all, the term “Rug Pull” refers to the theft of users’ funds by project developers and their escape with these funds; In fact, money laundering is about “raising money” and in many cases the project manager is not caught.
In the absence of all sorts of traditional rules in the field of defa, users are forced to trust the platforms to which they bring cash or buy tokens, and unfortunately this trust is sometimes damaged by Rug Money scams.
Rug money is a scam, or more precisely, an “Exit Scam” in which developers create a new token, create a trading pair with a major currency such as Tetra, and open a pool of liquidity from the pair.
The project manager then starts marketing new tokens and encourages people to deposit in the pool by promising high profits. When a significant amount of the currency enters the pool, Diffie developers use the escape routes already embedded in their smart contracts and run away with people’s money. These exit methods are codes deliberately placed in smart contracts and used to multiply millions of new tokens and sell them for a popular currency. These exit routes are called Back Door or “Door”.
The project manager picks up the proposed currency that the investors have brought into the pool, leaving only millions of worthless tokens in the pool. As we have said, in most cases, the developer or the owner of the project does not leave a trace and mostly the hands of the investors do not go anywhere.
One example of this type of scam was the multi-billion dollar Rugby Sushi Swap in 2020. In this rag money, an anonymous Sushi Swap developer called Chef Nomi, after collecting billions of dollars in user bail, cashed in on his sushi tokens without notice.
As a result, the price of sushi tokens fell to near zero; This event has been called one of the “most dramatic moments in the field of defense”.
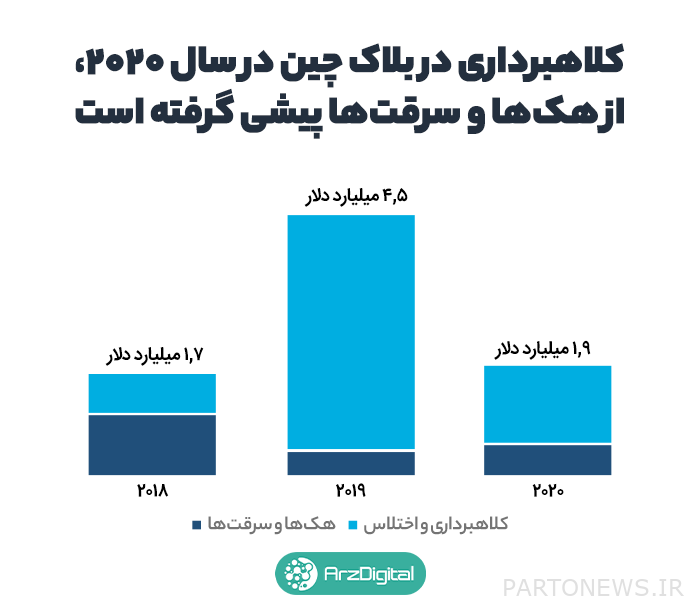
Scams are a billion-dollar industry, and despite the efforts of developers to reduce the risks in this area, these scams are still common. In the second half of 2020, 99% of all blockchain-based scams in China accounted for money diffusers and exit scams.
How to stay away from these 3 big threats on defy platforms?
Despite the rapid growth of this type of subversive activity, there are ways to assess the risk in a company before investing, here are a few examples:
- Check team credibility in other projects
- Careful study of project white paper
- Check if the project coding has been checked by people other than the project team members
- Sensitivity to existing warnings (such as promises of unrealistic returns or excessive advertising and marketing costs).
Ultimately, the very designs that address the need for defy protocols for intermediaries and give them the ability to revolutionize the financial industry make them vulnerable to theft.
Limited regulatory rules, along with the open source nature of the Chinese blockchain, mean that there are vulnerabilities in lending protocols that hold large amounts of money; But like the rest of China’s blockchain industry, defaults are expected to be minimized over time.

